Equity mutual funds have become a cornerstone for investors aiming to grow their wealth over time. With their potential for higher returns, these funds appeal to those willing to accept a certain level of risk in exchange for market-linked growth. But what exactly is an equity mutual fund, and what types are available? Let’s dive in.
What is an Equity Mutual Fund?
An equity mutual fund is a type of mutual fund that primarily invests in the shares of companies listed in the stock market. According to regulatory norms, equity funds must allocate at least 65% of their assets to equities. These investments are diversified across various sectors, industries, and market capitalizations to balance risk and returns.
The fund manager actively monitors and adjusts the portfolio to maximize returns based on market trends and economic conditions. Equity mutual funds are ideal for investors with a long-term horizon who are seeking capital appreciation rather than steady income.
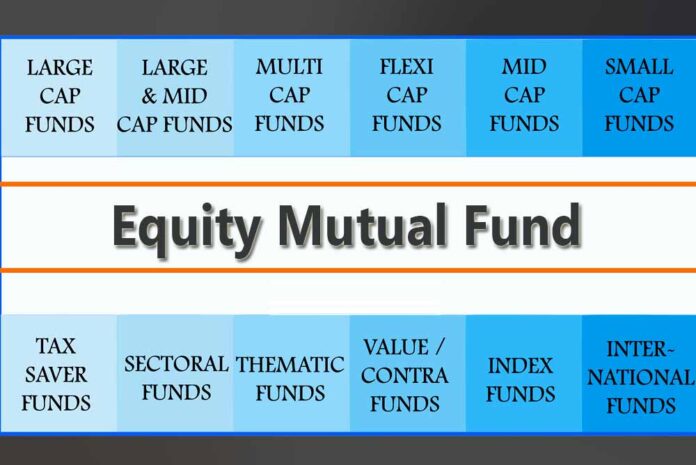
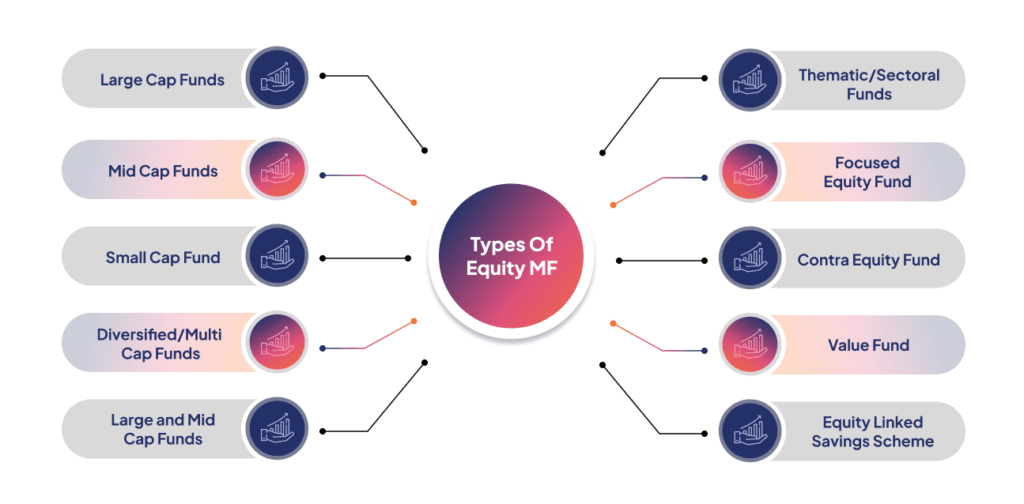
Types of Equity Mutual Funds
Equity mutual funds are broadly classified based on their investment strategies, market capitalization, and sectors. Here are the key types:
1. Large-Cap Funds
Large-cap funds invest predominantly in well-established companies with a large market capitalization, often the top 100 companies in terms of market value. These companies are leaders in their respective industries and provide relatively stable returns. While the growth potential may be moderate, the risk is generally lower compared to mid-cap and small-cap funds.
Suitability: Best for conservative investors seeking stability and steady growth.
2. Mid-Cap Funds
Mid-cap funds focus on investing in mid-sized companies, ranked between 101 and 250 in market capitalization. These companies offer a blend of growth potential and risk. While they may not have the stability of large-cap companies, their growth prospects are often higher, making them suitable for investors with a moderate risk appetite.
Suitability: Suitable for investors seeking a balance between growth and risk.
3. Small-Cap Funds
Small-cap funds invest in smaller companies that rank beyond the top 250 in market capitalization. These funds have significant growth potential but come with higher risk due to the volatility associated with smaller companies. They are best suited for aggressive investors with a long-term investment horizon.
Suitability: Ideal for aggressive investors willing to tolerate high volatility.
4. Multi-Cap Funds
Multi-cap funds provide exposure to a mix of large-cap, mid-cap, and small-cap stocks. This diversified approach allows the fund manager to allocate assets dynamically based on market opportunities. Multi-cap funds offer a balanced risk-return profile, making them a popular choice for investors.
Suitability: Suitable for investors seeking diversification across market caps.
5. Flexi-Cap Funds
Flexi-cap funds are similar to multi-cap funds but come with more flexibility in allocation. The fund manager can invest across market caps without restrictions, based on market conditions.
Suitability: Best for investors who want a flexible, dynamic allocation strategy.
6. Sectoral and Thematic Funds
These funds invest in specific sectors such as technology, healthcare, or energy, or follow a theme such as ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance). Sectoral funds are high-risk investments as their performance depends heavily on the chosen sector’s market performance.
Suitability: Suitable for seasoned investors with a strong understanding of specific sectors or themes.
7. Value Funds
Value funds focus on undervalued stocks that have the potential for long-term growth. The aim is to generate returns by investing in stocks trading below their intrinsic value.
Suitability: Ideal for investors with a long-term horizon who prefer a value investing approach.
8. Thematic Funds
Thematic funds invest in stocks based on a particular theme, such as digital transformation, green energy, or infrastructure. Unlike sectoral funds, thematic funds can span multiple sectors within a theme.
Suitability: Best for investors who understand and believe in a specific investment theme.
9. International Funds
International funds invest in stocks of companies listed in foreign markets. These funds provide geographical diversification and exposure to global growth opportunities.
Suitability: Suitable for investors looking to diversify their portfolio globally.
10. ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Scheme)
ELSS funds are tax-saving equity mutual funds that come with a lock-in period of three years. They qualify for tax deductions under Section 80C of the Income Tax Act. ELSS funds primarily invest in equities and are an excellent option for investors looking to grow their wealth while saving on taxes.
Suitability: Ideal for investors seeking tax benefits along with equity growth.
11. Focused Funds
Focused funds invest in a limited number of stocks, usually around 20-30, allowing the fund manager to concentrate on high-conviction picks. While this focus can lead to higher returns, it also increases risk due to limited diversification.
Suitability: Suitable for investors willing to take concentrated risks for potentially higher returns.
12. Index Funds
Index funds aim to replicate the performance of a specific index, such as the Nifty 50 or Sensex. These funds are passively managed and come with lower expense ratios. While they lack the flexibility of actively managed funds, they offer steady returns that closely mirror the chosen index.
Suitability: Best for investors looking for low-cost, steady returns.
13. Dividend Yield Funds
These funds invest in companies known for paying high dividends. The focus is on generating regular income along with potential capital appreciation. Dividend yield funds are suitable for conservative investors who prefer periodic returns.
Suitability: Ideal for investors seeking regular income along with moderate growth.
14. Rajiv Gandhi Equity Savings Scheme (RGESS)
RGESS funds were introduced to encourage first-time retail investors to invest in the equity market. These funds offer tax benefits and focus on equity investments in large-cap stocks and ETFs.
Suitability: Best for first-time investors looking to save taxes and enter the equity market.
How to Choose the Right Equity Mutual Fund?
Choosing the right equity mutual fund depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and investment horizon. Here are a few tips:
- Understand Your Goals: Are you investing for long-term wealth creation, short-term gains, or tax-saving purposes?
- Assess Risk Appetite: Large-cap funds suit conservative investors, while small-cap funds are ideal for aggressive ones.
- Analyze Past Performance: While past performance is not a guarantee of future returns, it provides insights into the fund’s consistency and reliability.
- Check Expense Ratio: Lower expense ratios can enhance your net returns.
Conclusion
Equity mutual funds offer a range of options to cater to different investment needs and risk profiles. Whether you are a conservative investor seeking stability or an aggressive investor aiming for high growth, an equity mutual fund is tailored for you. Understanding the types of equity mutual funds can help you make informed decisions and align your investments with your financial objectives.
Other Articles:
MF Central: How can mutual-fund investors use MF Central? It’s Features?